Types
 | PNP |  | P-channel |
 | NPN |  | N-channel |
| BJT |
| JFET |
|
 | 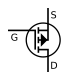 |  | 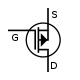 | P-channel |
 | 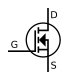 | 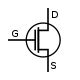 |  | N-channel |
| JFET | MOSFET enh | MOSFET dep |
Transistors are categorized by
- Semiconductor material: graphene, germanium, silicon, gallium arsenide, silicon carbide, etc.
- Structure: BJT, JFET, IGFET (MOSFET), IGBT, "other types"
- Polarity: NPN, PNP (BJTs); N-channel, P-channel (FETs)
- Maximum power rating: low, medium, high
- Maximum operating frequency: low, medium, high, radio frequency (RF), microwave (The maximum effective frequency of a transistor is denoted by the term fT, an abbreviation for "frequency of transition". The frequency of transition is the frequency at which the transistor yields unity gain).
- Application: switch, general purpose, audio, high voltage, super-beta, matched pair
- Physical packaging: through hole metal, through hole plastic, surface mount, ball grid array, power modules
- Amplification factor hfe (transistor beta)[14]
Thus, a particular transistor may be described as
silicon, surface mount, BJT, NPN, low power, high frequency switch.










No comments:
Post a Comment